Grace Score Heart
Link To And Excerpts From The Heart Score For Major Cardiac Events On Mdcalc Tom Wade Md
Are We Missing Acute Mis With Clinical Risk Scores Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
The Heart Score A New Ed Chest Pain Risk Stratification Score Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
Make Copies Of Heart Score Slide Chest Pain Differential Ppt Video Online Download

Full Text Clinical Decision Aids For Chest Pain In The Emergency Department Ide Oaem
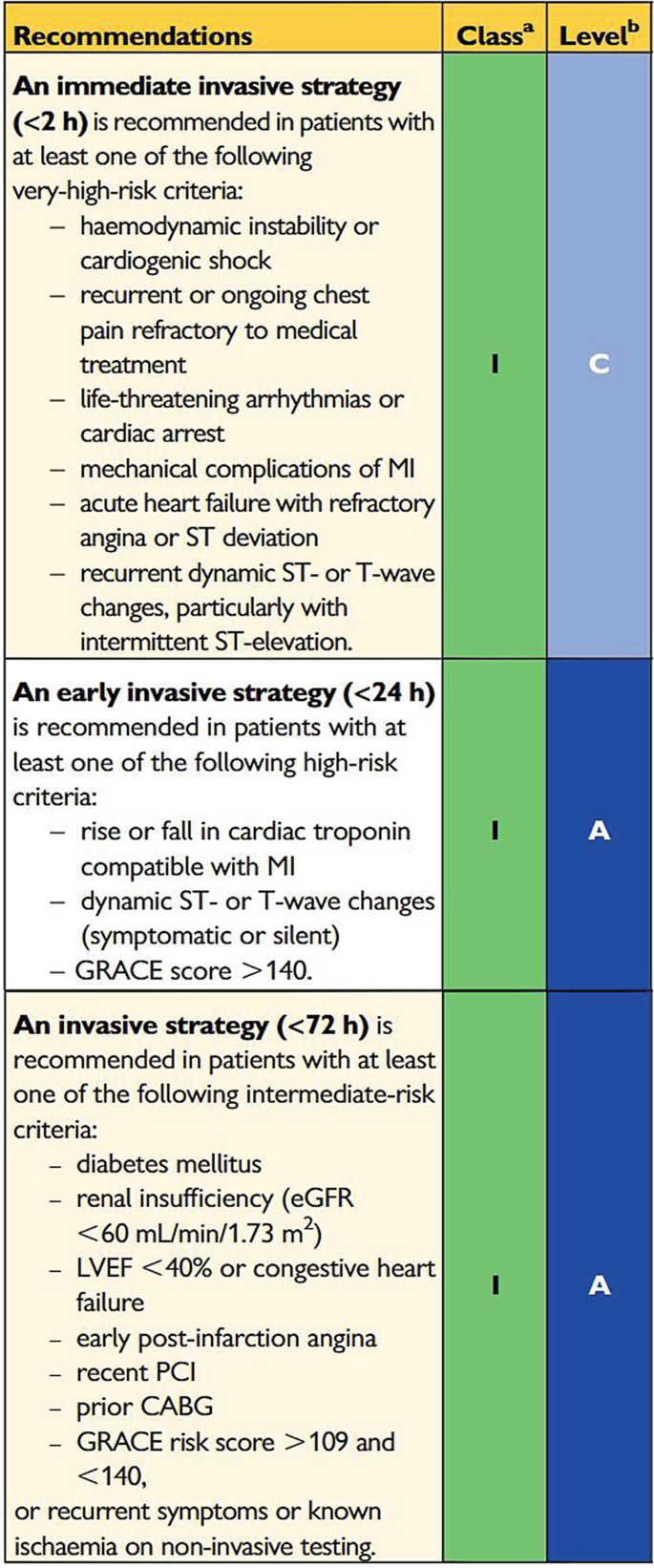
Indications For An Early Invasive Strategy In Nste Acs Patients Springerlink
Vancouver Chest Pain Rule;.
Grace score heart. We investigated whether the at-discharge Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score predicts heart failure admission following ACS. 2–5 The score applies clinical variables, the electrocardiogram, and cardiac. The HEART score identified 381 patients as "low risk" with 0.8% missed MACE.
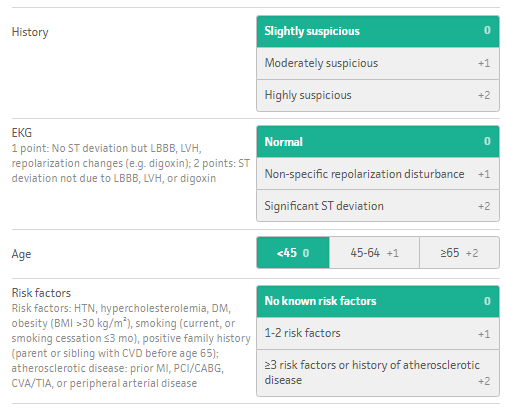
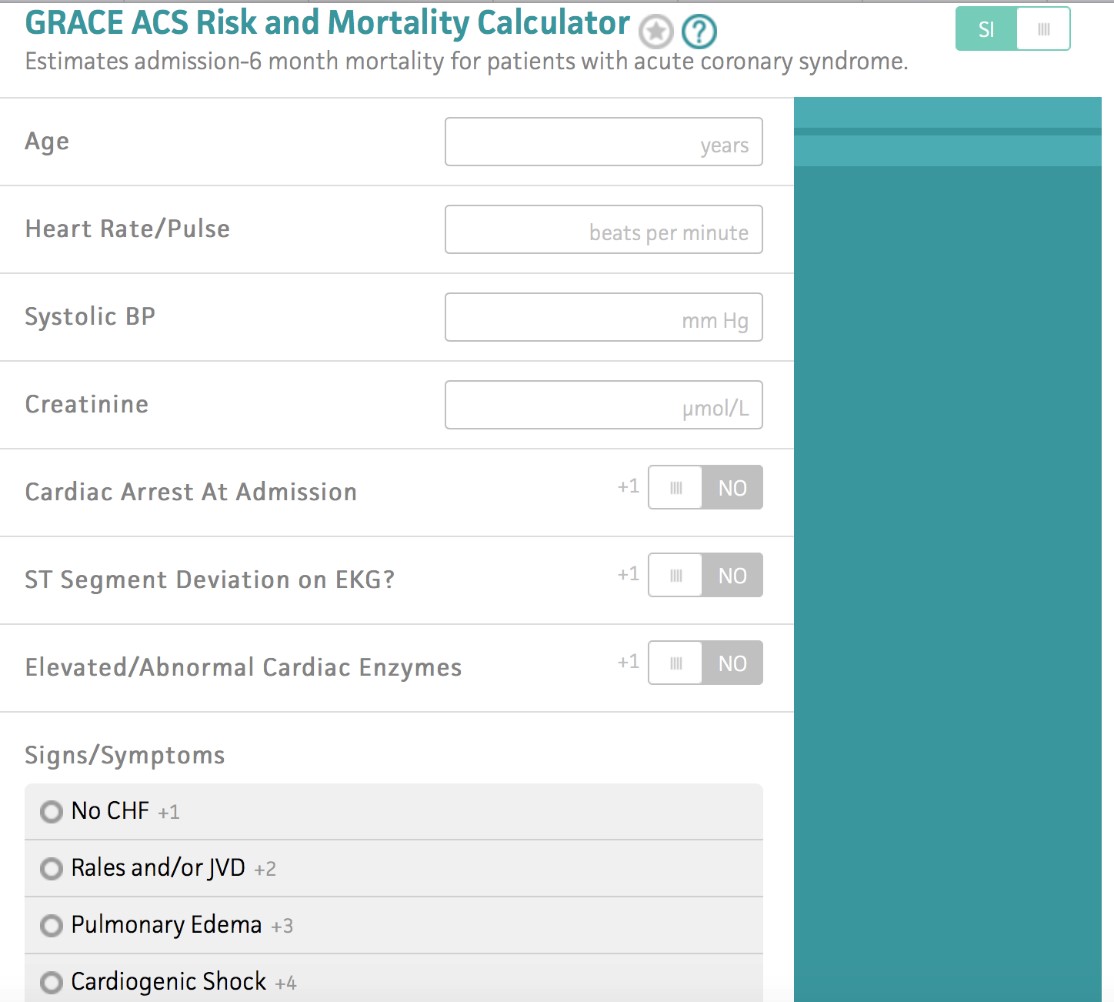
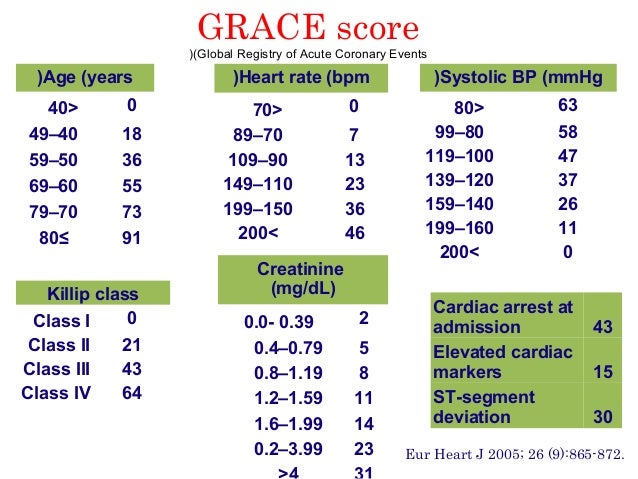
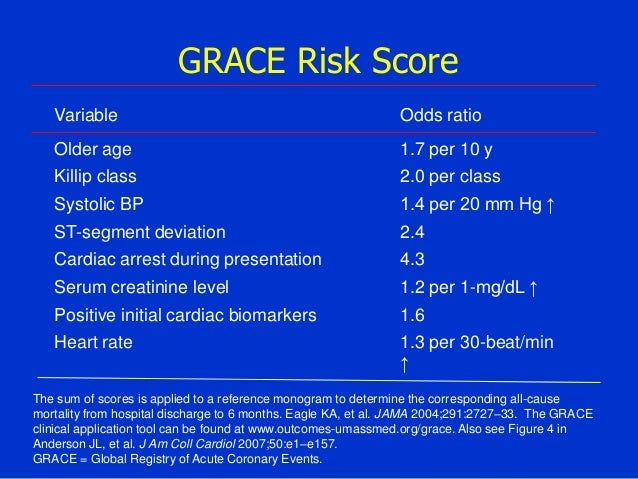
Using the GRACE risk score, eight factors independently predict risk of heart attack and/or death:. The HEART score predicts 6 week risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) based on patient age and medical history, ECG findings, troponin levels and the presence of specific heart disease risk factors (Hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, obesity). This system has incorporated more dynamic features like heart rate, blood pressure, survival from cardiac arrest, serum creatinine.
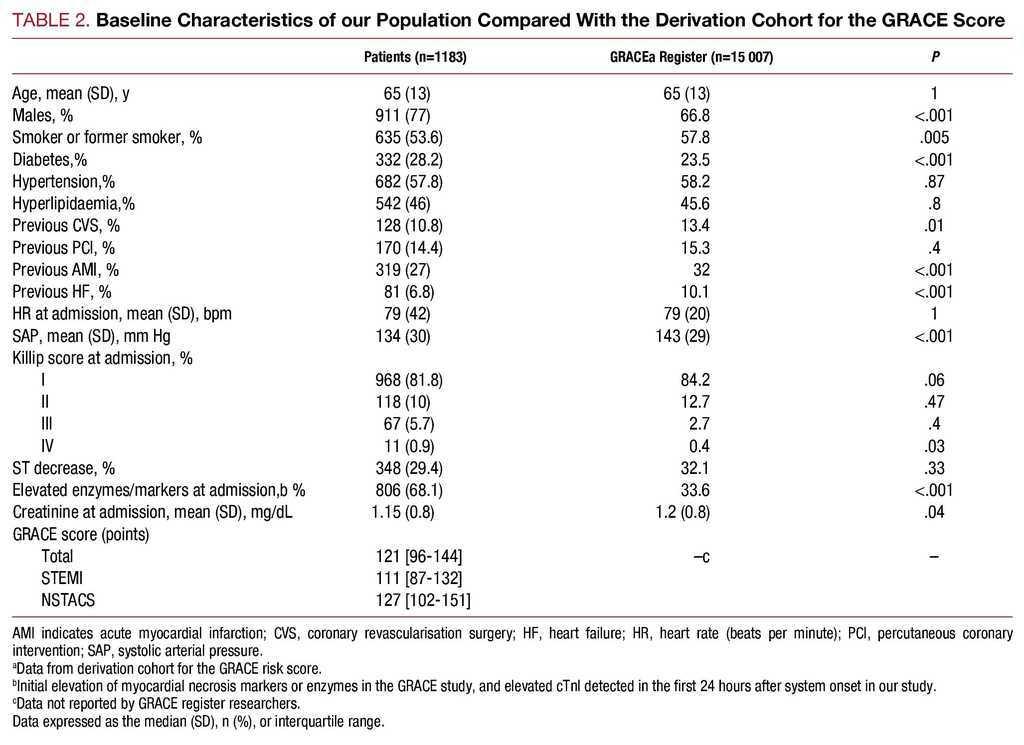
1 To improve prognostication and promote consistency in the investigation and management of patients with acute coronary syndrome, the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score was developed. Presence of CAD was confirmed or excluded by either visual coronary angiography or CT coronary angiography. Primary end point is the evidence of significant coronary artery disease needing medical.
A GRACE score will determine whether the cardiac event is low, medium, or high risk. In addition, GRACE "modestly predicted" in-hospital, 30-day, and 90-day mortality, while TIMI and TARRACO did not predict all-cause mortality. 2.5% risk of adverse cardiac event.
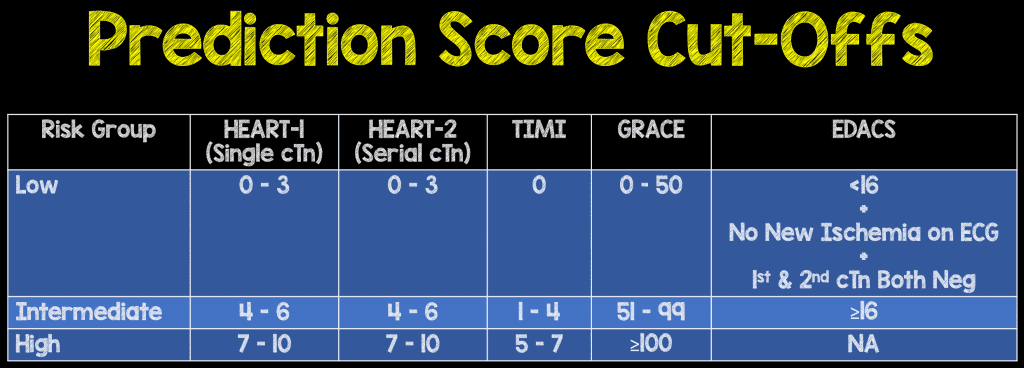
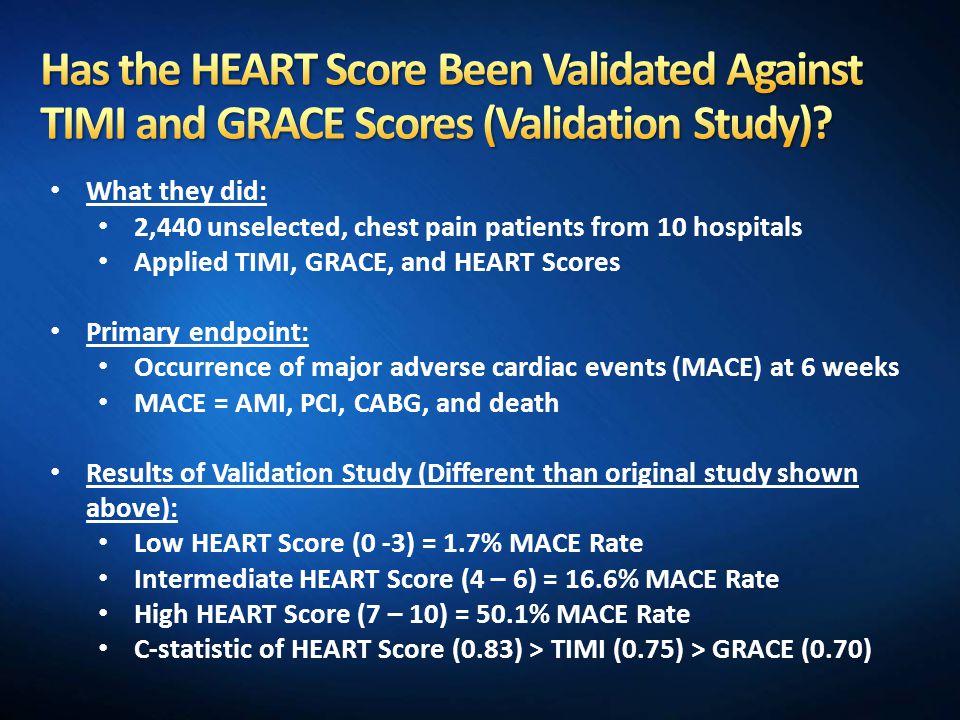
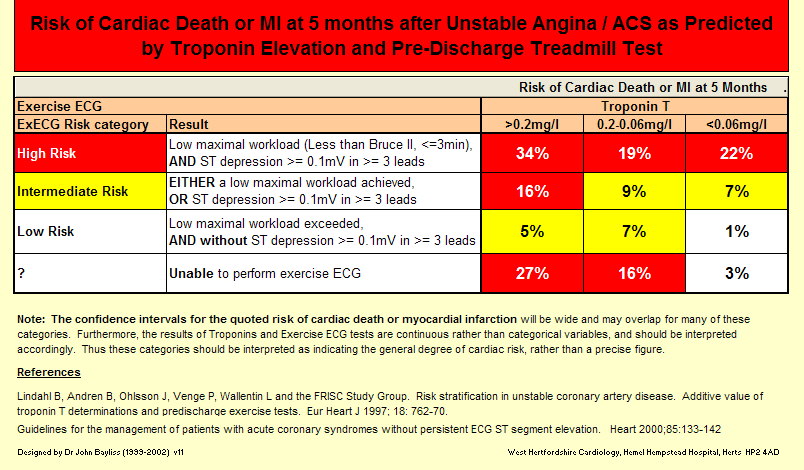
Using a single contemporary cTn at presentation, a HEART score of ≤3 demonstrated sensitivity and NPV of ≥99.5% for 30-day MACE. Intermediate HEART Score (4 – 6) = 16.6% MACE Rate;. The combined risk of death or MI at 1 year is also given.
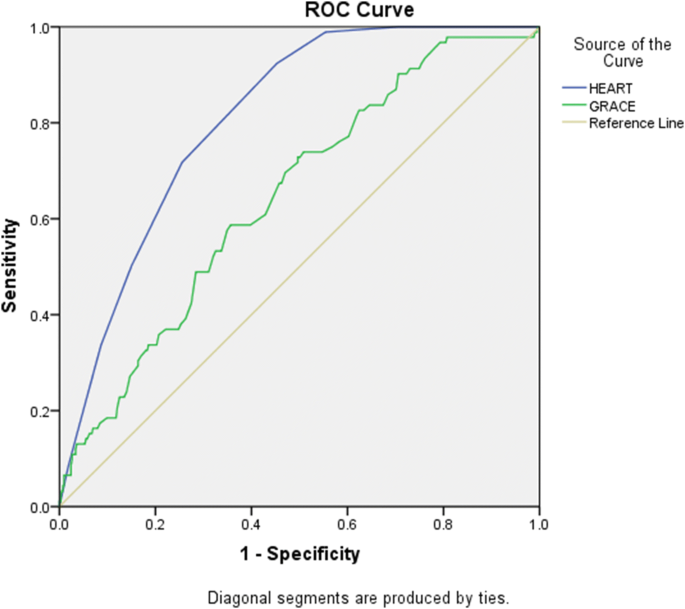
The HEART score was developed in order to risk stratify these patients. The GRACE score at 6 months is also provided as guidelines have categorized patients into low (≤108 GRACE score), medium (109–140 GRACE score) and high risk (>140 GRACE score) (ESC Guideline on non-STE ACS 11. HEART score had better accuracy at identifying patients at high risk for mortality and is a better predictor of MACE at the end of 1 days in patients presenting with CP to ED when compared to TIMI and GRACE scores.
0.84-0.%) and 0.80 (95% CI:. In 11 the GRACE risk score was made available as an app, and it has since been. This score uses these eight parameters to calculate risk:.
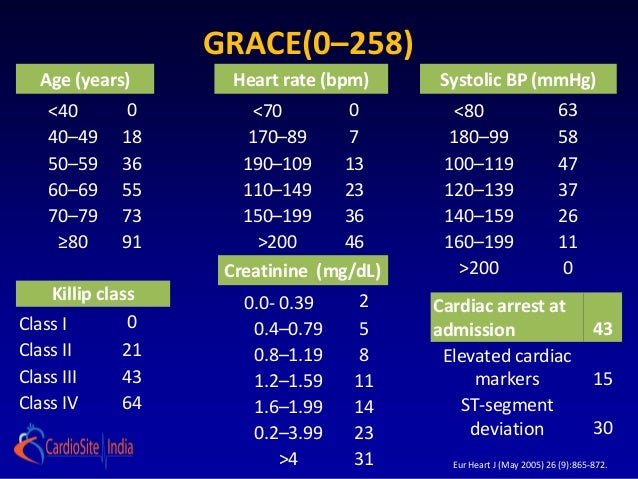
Results showed the mean GRACE, TIMI and TARRACO scores were 140±31, 3.7±1.4, and 4.9±2.2, respectively. The Killip classification consists of 4 classes based on clinical symptoms. The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk score is widely recommended for risk assessment in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Grace of my Heart is loosely based on the life of real life singer/songwriter Carol King who yearns to break free of her privileged suburban upbringing to. "GRACE Score for Heart Attack:. We'll also occasionally use the GRACE score on our high risk NSTEMI patients to consider doing early invasive management as opposed to delayed intervention in our NSTEMI patients.
3.6% (12/334) 2.0% (14/708) 3.2% (14/439) MACE, of which AMI:. Renal insufficiency (glomerular filtration rate < 60mL/min/1.73m2) Left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 40 %;. Study performed on patient population from the Netherlands;.
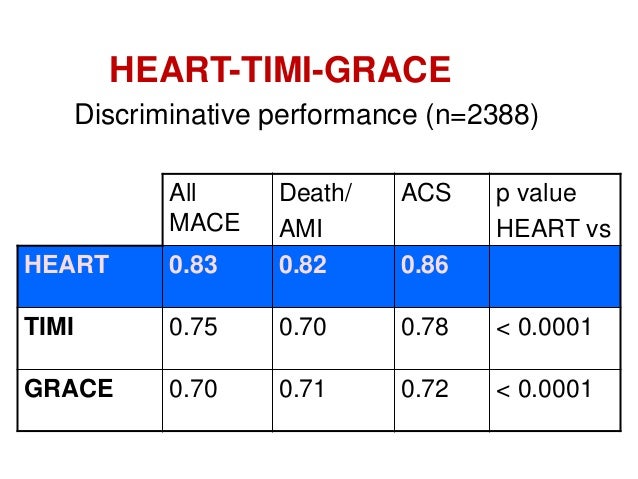
HEART outperformed both TIMI and GRACE in overall discriminative capacity for 30-day MACE. Your doctor might use it to help manage your condition and make decisions about your. Events in-hospital for the GRACE risk score (RS), at 14 days for the TIMI RS, and at 30 days for the PURSUIT RS.
Primary end point is the evidence of significant coronary artery disease needing treatment. Framingham Heart Failure Diagnostic Criteria;. 1,1 patients in HEART care period, of which 1,748 (96%) patients with risk scores calculated and follow-up 54% male, mean age 62 MACE incidence 19% AUCs:.
We haven't had any bad outcomes and we've also saved a number of ICU beds this way for other patients that need ICU-level care. Its emergence has received widespread international media coverage. TIMI and GRACE are the risk scores that up until now have been most extensively investigated, with GRACE performing better.
0.78-0.%), respectively (all differences in AUC highly statistically significant). This score uses these eight parameters to calculate risk:. High HEART Score (7 – 10) = 50.1% MACE Rate;.
Audience Score User Ratings:. Ottawa Heart Failure Risk Score. Six AJ, Backus BE, Kelder JC.
Drugs that are commonly given. If the GRACE score indicates a person is a low risk after an NSTEMI, a doctor may prescribe medication. Risk Management" app is designed to help fellow health care practitioner to assess the mortality risk in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients.
At an absolute level of safety of at least 98% sensitivity, the GRACE score identified 231 patients as "low risk" in which 2.2% a MACE was missed;. 6 months mortality (and mortality/MI). GRACE, HEART and TIMI score Mnemonics :.
Sometimes compared to TIMI Score for UA/NSTEMI and the GRACE ACS Risk Score (older ACS scores), but the latter two differ from the HEART in that they measure risk of death for patients with diagnosed ACS. GRACE scoring system The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) scoring system is the latest and has originated from GRACE registry data.5 It is a relatively complex scoring system and needs a computer or personal digital assistant for proper calculation. 334/1748 (19.1%) 708/1748 (40.5%) 439/1748 (25.1%) Percentage of MACE in “low risk” group:.
The GRACE risk score stratifies mortality risk (6 mo – 3 y) from myocardial infarction (ST- elevation and non-ST elevation) in patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome. The predictor variables used are age, heart rate (HR), systolic blood pressure (SBP), serum creatinine, Killip heart failure class, the existence or not of cardiac arrest at admission, any deviations of the ST segment and cardiac enzyme levels. When comparing the GRACE, TIMI and HEART in terms of predictive values for low- and high-risk, and the c-statistics, we conclude that the HEART score is the best score for the group of all cause chest pain patients at the emergency department and that GRACE and TIMI should be reserved for ACS patients in the CCU.
It predicts 30-day mortality after myocardial infarction. GRACE comes from the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events, an international ACS database and is calculated at hospital admission and at discharge. Receiver Operated Characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to determine discriminative power of each of the.
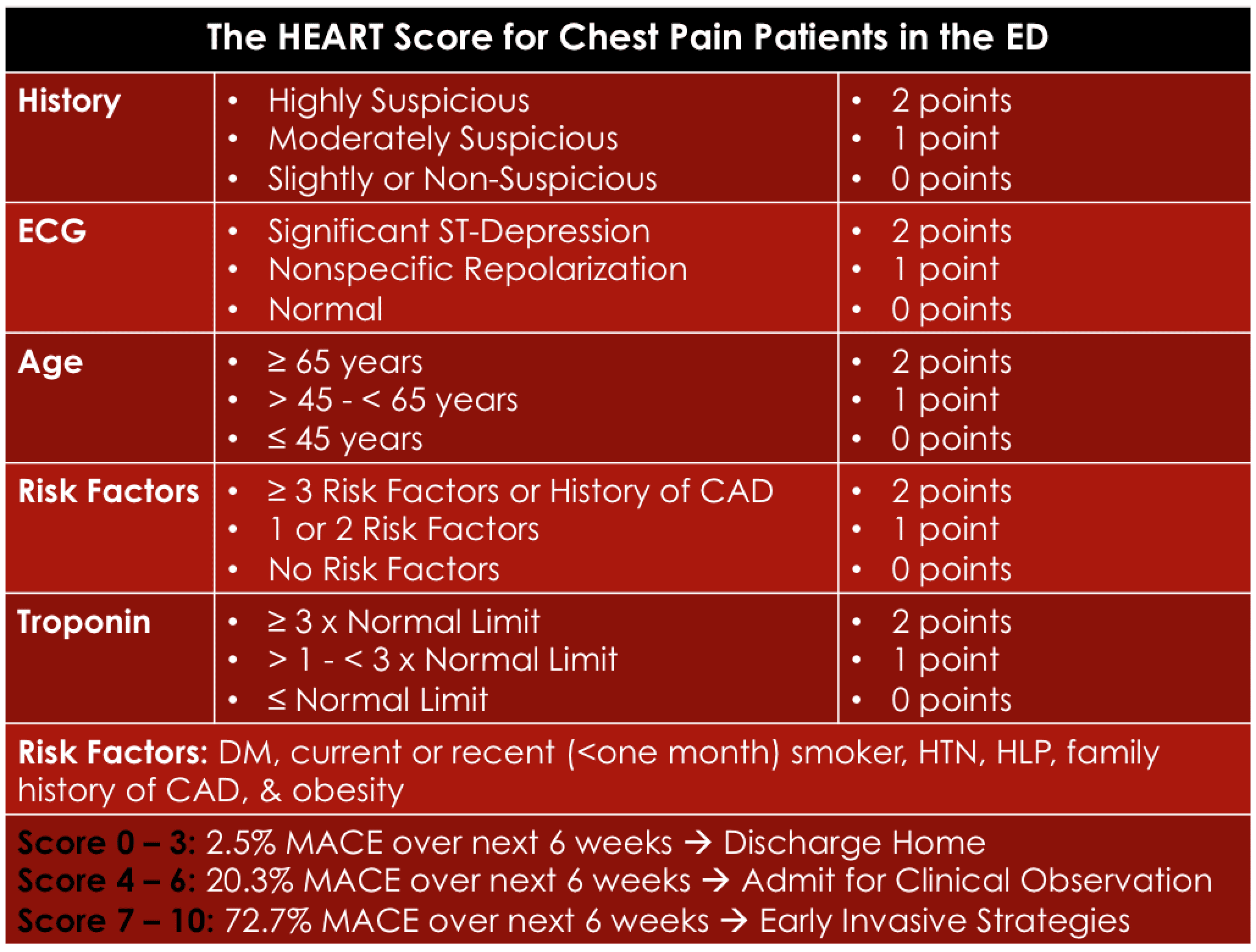
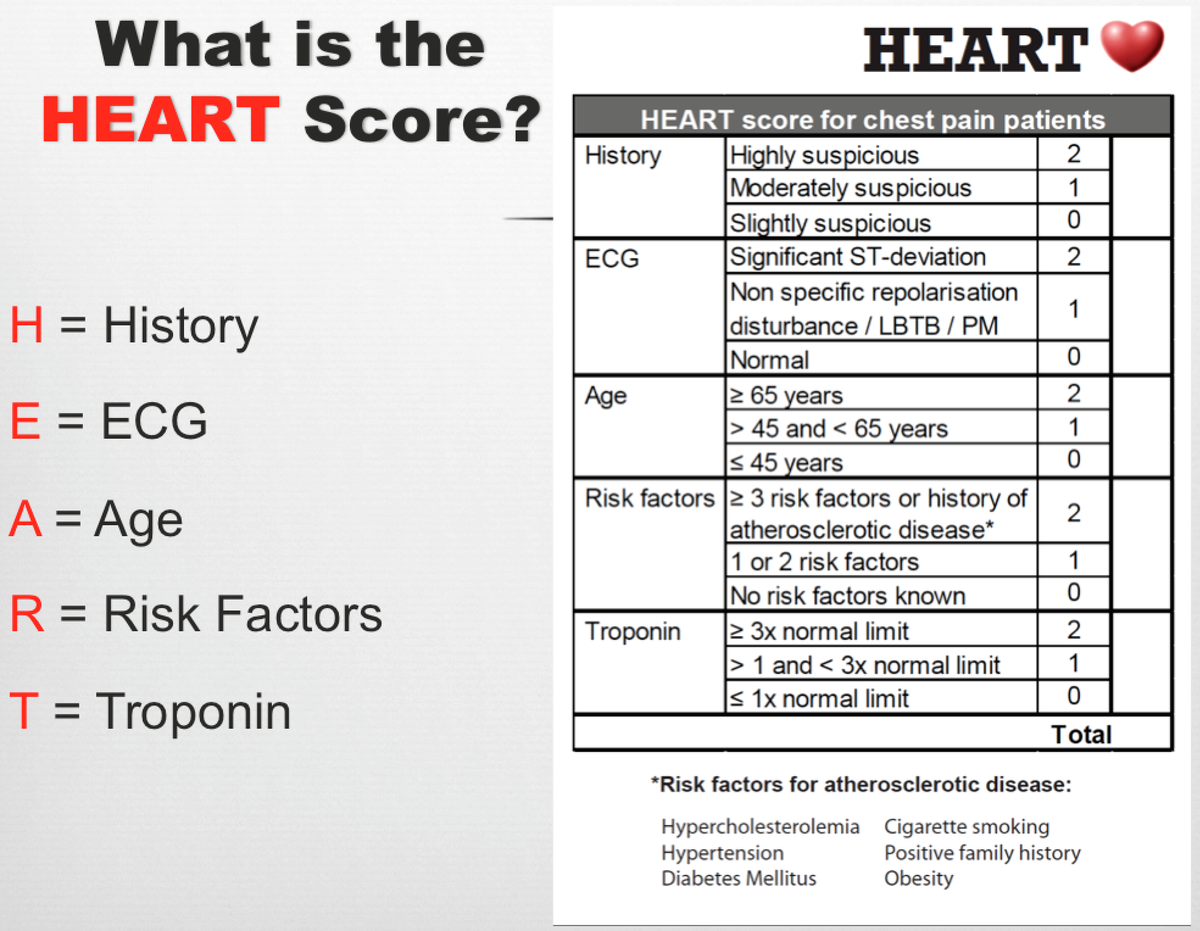
This GRACE risk score calculator includes both ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non ST segment elevation (non-STEMI). Unlike other clinical decision rules, the components are scored 0, 1, or 2, allowing for a middle ground, and this CDR was uniquely developed for use in the ED. The score is an acronym for history, EKG, age, risk factors, and troponin.
All these scores were developed for short-term prognosis:. In-hospital mortality (and mortality/MI). GRACE ACS Risk Model.
The TIMI risk score is a tool that doctors use to predict the chances of having or dying from a heart event. 45 patients lost to follow up;. The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score, Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk index and Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa in Unstable angina 3.
Chronic hyperglycemia hemoglobinA1c (HbA1c) can independently predict major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) in patients with ACS. Patients with NSTEACS who have both of:. Both HEART score and GRACE scores were calculated on each patient and stratified into low, intermediate and high risk of MACE in both indexes.
Cardiac Chest Pain Risk Stratification Epomedicine Oct 18, No Comments Cardiovascular system Internal medicine Last modified:. The more recent Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score was developed from the registry, 8 with a population of patients across the entire spectrum of ACS. No comparison of Heart Score to clinical gestalt.
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a common and preventable complication of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It has been widely reported to outperform the TIMI and the GRACE scores (4,18,19). GRACE Score 2.0 Calculator.
Using the GRACE risk score, eight factors – age, heart rate, systolic blood pressure, renal function, congestive heart failure, ST-segment deviation, cardiac arrest and elevated biomarkers – independently predict risk of heart attack and/or death. Coronary artery bypass grafting;. The most reputed are the TIMI, PURSUIT and GRACE risk scores, which were compared by De Araújo Gonçalves.
(GRACE score >140, dynamic ST -segment and/or T-wave changes on ECG, or rise and/or fall in troponin compatible with MI) an early invasive strategy is recommended (within 24 hours of admission). HEART, GRACE and TIMI scores were calculated from data obtained on patient attendance, with subjective aspects entered by the attending medical practitioner in real time. Nevertheless, ACS risk scores have not been shown to predict CHF risk.
Coronary heart disease is responsible for around 2 million deaths across Europe every year. The scores can be stratified between:. HEART Score The score has been derived and validated in an ED population and predicts 6 week adverse cardiac events Low risk patients have a score 0-3 and have a less than 2% risk of MACE at 6 weeks.
Based on a global registry of 102,341 patients, the GRACE score estimates in-hospital, 6 months, 1 year, and 3-year mortality risk after a heart attack. Killip class, or signs of heart failure from a physical exam;. Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score.
Corresponding cut-off for “low risk” ≤ 72 points ≤ 3 points:. “In the literature, several risk scores for nSTE-ACS have been published. Reynolds CAD Risk TIMI Risk Score (STEMI) VALIANT Heart Failure Risk Score GRACE The GRACE ACS risk calculator estimates risk of death following acute coronary syndrome (ACS) Pre-test probability of CAD (CAD consortium) Determine pre-test probability of coronary artery disease in patients with chest pain.
Those with a score of 130 or higher go to the ICU after catheterization, and those with lower scores can go to our step down unit. 0.70-0.76%), 0.86 (95% CI:. C-statistic of HEART Score (0.) > TIMI (0.75) > GRACE (0.70) Limitations:.
The HEART score has five prognostic factors, namely history, ECG, age, risk factors, and troponin. GRACE Score, Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events Score, ACS Risk Model, Acute Coronary. GRACE score HEART score TIMI score;.
Each ED had different cut-off values for positive troponins;. The HEART Score outperforms the TIMI Score for UA/NSTEMI, safely identifying more low-risk patients. The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk score is recognised internationally as a tool for the risk stratification of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes,1–7 and its use in routine clinical practice is recommended by the European Society of Cardiology and the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE).8, 9 Because it collects patient.
Five-year mortality and hospitalization. The AUC of GRACE, HEART, and TIMI were 0.73 (95% CI:. GRACE score >109 and <140;.
In 11 the GRACE risk score was made available as an app, and it has since been downloaded more than 10,000 times. The score is addressed to patients presenting to ER with chest pain. Chest pain in the emergency room:.
Eur Heart J 11;32:2999–3054). Different from the TIMI and the GRACE scores, the HEART score was specifically developed for chest pain patients in the ED (14,). Both HEART score and GRACE scores were calculated on each patient and stratified into low, intermediate and high risk of MACE in both indexes.
NYHA Heart Failure Classification;. The Heart Score was developed in an ED setting in all patients with chest pain and not just ACS patients. There is a GRACE risk score for the estimation of in-hospital mortality and another for mortality in the period from the time of hospital discharge up to 6 months.
CHF Decision Rule for Predicting Mortality;. Comparison of GRACE, HEART and TIMI score in predicting ACS in acute chest pain patients Results:. Value of the HEART score.
A Comparison of The HEART, TIMI and GRACE Risk Scores in The Prediction of a Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE) in Undifferentiated Emergency Patients with Cardiac Chest Pain Author:. An early routine invasive approach within 24 hours of admission is recommended for NSTEMI based on hs-cTn measurements, GRACE risk score >140, and dynamic new, or presumably new, ST-segment changes, as it improves major adverse cardiac events and possibly early survival. The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score estimates the risk of death or death/myocardial infarction (MI) in patients following an initial acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
It helps us determine disposition in our STEMI patients;. Troponin-Only Manchester Acute Coronary Syndrome Decision Aid;. Framingham Cardiac Risk Scale Framingham Heart Failure Diagnostic Criteria Goldman Criteria for ICU Chest Pain Admission GRACE Score Heart Auscultation Heart Murmur Heart Rate HEART Score Home Blood Pressure Monitor Hypotension J Point J Wave.
Presence of CAD was confirmed or excluded by either visual coronary angiography or CT coronary angiography. Number of patients classified “low risk” / total number of patients:.
Validation Of The Grace Risk Score For Predicting Death Within 6 Months Of Follow Up In A Contemporary Cohort Of Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition
The Heart Score A New Ed Chest Pain Risk Stratification Score Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog

Full Text Comparison Of Nine Coronary Risk Scores In Evaluating Patients Present Ijgm

Full Text Comparison Of Nine Coronary Risk Scores In Evaluating Patients Present Ijgm

Components Of The Timi Ua Nstemi Grace Non Ste Acs And Heart Scores Download Table

Mortality And Cardiovascular Morbidity Within 30 Days Of Discharge Following Acute Coronary Syndrome In A Contemporary European Cohort Of Patients How Can Early Risk Prediction Be Improved The Six Month Grace Risk Score
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationthe Clinical Decision Rules Series Part 3 Clinical Pathway Use Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Grace Risk Score And Outcomes Low Intermediate And High Categories Download Table
Cardiovascular Events In The Era Of High Sensitivity Troponin
Risk Stratification Of Ua Nstemi

High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I And Clinical Risk Scores In Patients With Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome Circulation
The Heart Score A New Ed Chest Pain Risk Stratification Score Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
Plos One Grace Score Among Six Risk Scoring Systems Cadillac Pami Timi Dynamic Timi Zwolle Demonstrated The Best Predictive Value For Prediction Of Long Term Mortality In Patients With St Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Www Acc Org Media Non Clinical Files Pdfs Excel Ms Word Etc Meetings 18 Course Pdfs Middle East Friday 1600 Acc10shaibi Pdf La En Hash 5fcf7e57babc2234facc4f8cbf232f122ab

Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcurrent Ed Management Of Non St Segment Elevation Mi Nstemi A Practice Update Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Comparison Of Performance Of Grace Score Heart Score And Timi Score In Download Table

Grace Score Phoenix Cardiology
Umem Org Files Uploads International Journal Of Cardiology 13 Backus Pdf

Ccu Grace Score Ccu Stratify Grace Acs Facebook
Plos One Grace Score Among Six Risk Scoring Systems Cadillac Pami Timi Dynamic Timi Zwolle Demonstrated The Best Predictive Value For Prediction Of Long Term Mortality In Patients With St Elevation Myocardial Infarction

The Global Registry Of Acute Coronary Events 1999 To 09 Grace Heart

Ccu Home Facebook
Salim R Rezaie Md على تويتر Heart Score Is Superior To Timi Grace Scores In An Undiff Cp Pt Population In The Ed Http T Co Iqbay2zrvl Foamed Http T Co Rzpxtdcpc9

Heart Score For Predicting Adverse Outcomes In Patients With Chest Pain Letters To The Editor American Family Physician
The Slide Set

Pdf Version Heartmirror Com

Modified Heart Score Improves Early Safe Discharge For Suspected Acute Coronary Syndromes A Prospective Cohort Study With Recalibration Of Risk Scores To Undetectable High Sensitivity Troponin T Limits Jacc Journal Of
Q Tbn 3aand9gcstw5 154ytundhg1wfgp7kqyokunovroyrnxgtesgtc M5qo77 Usqp Cau

Risk Scores Timi Score 28 Chest Pain Section Grace Score 29 And Download Table
Http Www Crtonline Org Assets Dbee484c 7426 47ff 9a01 Dfc9ff9 Verdict Engstrom Pdf

The Grace Risk Score Assessing Heart Attack Risk And Guiding Treatment The University Of Edinburgh

My Latest Paper The Value Of The Grace Score For Predicting The Syntax Score In Patients With Unstable Angina Non St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Akbar Shafiee Md Msc

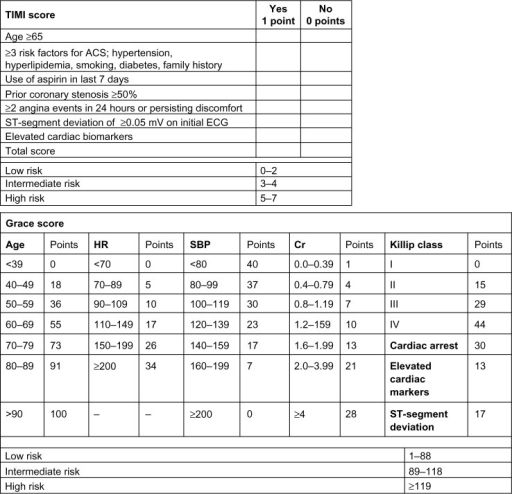
Timi Score And Grace Score Abbreviations Acs Acute Coronary Download Scientific Diagram

Evaluation Of The Impact Of The Grace Risk Score On The Management And Outcome Of Patients Hospitalised With Non St Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome In The Uk Protocol Of The Ukgris Cluster Randomised Registry Based

Pdf Comparison Of The Grace Heart And Timi Score To Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Chest Pain Patients At The Emergency Department Semantic Scholar
Umem Org Files Uploads International Journal Of Cardiology 13 Backus Pdf

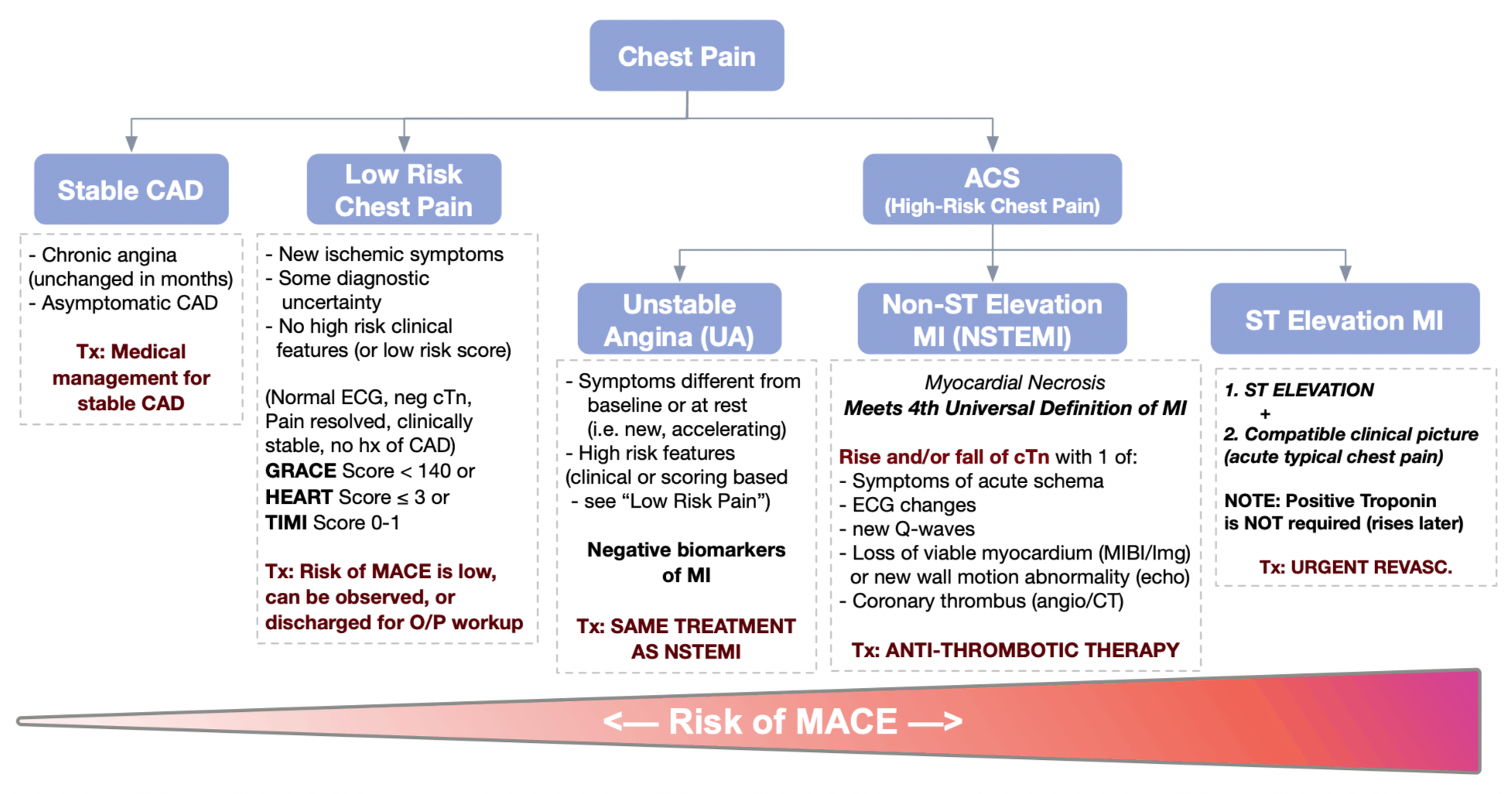
Fig 19 6 Acute Management Of Chest Pain And Acs Without St Segment Oxford Medicine Online

Acute Coronary Syndrome Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsgfnpz0ic9mt2zmea522fjqlwkcg1vqecmbw8zwc1 Qr0rk6cm Usqp Cau

Comparison Of The Grace Heart And Timi Score To Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Chest Pain Patients At The Emergency Department Sciencedirect

Six Years Of Heart Score Maryland 01 04
Plos One Does Simplicity Compromise Accuracy In Acs Risk Prediction A Retrospective Analysis Of The Timi And Grace Risk Scores

Ischaemic Heart Disease Ppt Download
Www Nwcscnsenate Nhs Uk Files 9014 5642 1864 Cmscn Nstemi Acs Guideline Final 16 Pdf

Heart Timi And Grace Scores For Prediction Of 30 Day Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events In The Era Of High Sensitivity Troponin

The Challenge Of Optimal Evaluation Of Low And Intermediate Pretest Probability Stable Chest Pain Insights From Recent Randomized Clinical Trials Upadhyayula S Kasliwal Rr J Clin Prev Cardiol

Improved Risk Stratification Of Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes Using A Combination Of Hstnt Nt Probnp And Hscrp With The Grace Score Semantic Scholar
Gale Academic Onefile Document Approach To Chest Pain And Acute Myocardial Infarction

Robert Robinson Tune My Heart To Sing Thy Grace Arr John Leavitt Sheet Music Pdf Notes Chords Sacred Score Satb Choir Download Printable Sku

Table 2 From Does Simplicity Compromise Accuracy In Acs Risk Prediction A Retrospective Analysis Of The Timi And Grace Risk Scores Semantic Scholar

Pdf Comparison Of The Grace Heart And Timi Score To Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Chest Pain Patients At The Emergency Department Semantic Scholar
Validation Of The Grace Risk Score For Predicting Death Within 6 Months Of Follow Up In A Contemporary Cohort Of Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition
Validation Of The Grace Risk Score For Predicting Death Within 6 Months Of Follow Up In A Contemporary Cohort Of Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition
Academic Oup Com Eurheartj Article Pdf 26 9 865 Ehi187 Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqb25e422edy7uwrbunrvofqaybotcirrdphr Ykqrl8q5sjnjm Usqp Cau
The Predictive Value Of The Heart And Grace Scores For Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Patients With Acute Chest Pain Springerlink
The Cardiology Library Zunis
Www Ed Ac Uk Files Atoms Files The Grace Risk Score Assessing Heart Attack Risk And Guiding Treatment 0 Pdf

Risk Stratification For The Development Of Heart Failure After Acute Coronary Syndrome At The Time Of Hospital Discharge Predictive Ability Of Grace Risk Score Journal Of Cardiology
Www Escardio Org Static File Escardio Education Live Events Courses Education Resource 003 1300 Bassand Wbz Mon S01a Pdf

Home Dr Deepak Natarajan
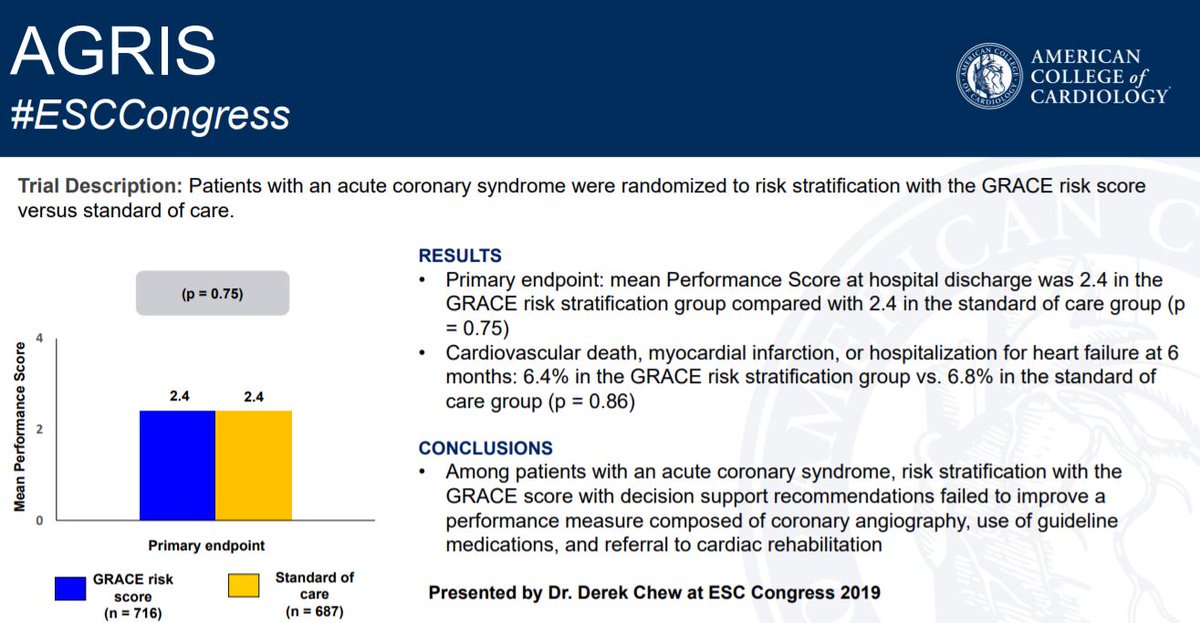
American College Of Cardiology Icymi The Agris Trial Failed To Show That Risk Stratification Grace Score With Decision Support Recommendations Was Superior To Standard Of Care T Co Yqnidzsi7d Esccongress T Co Wckql40arz

Comparison Of The Grace Heart And Timi Score To Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Chest Pain Patients At The Emergency Department Sciencedirect

State Of The Art Evaluation Of Emergency Department Patients Presenting With Potential Acute Coronary Syndromes Circulation
Academic Oup Com Eurheartj Article Pdf 38 41 3049 2143 Ehx492 Pdf

Mortality And Cardiovascular Morbidity Within 30 Days Of Discharge Following Acute Coronary Syndrome In A Contemporary European Cohort Of Patients How Can Early Risk Prediction Be Improved The Six Month Grace Risk Score
Acute Coronary Syndrome Nstemi
Www Escardio Org Static File Escardio Education Live Events Courses Education Resource 003 1300 Bassand Wbz Mon S01a Pdf

Rebel Em The Heart Score A New Ed Chest Pain Risk Stratification Score
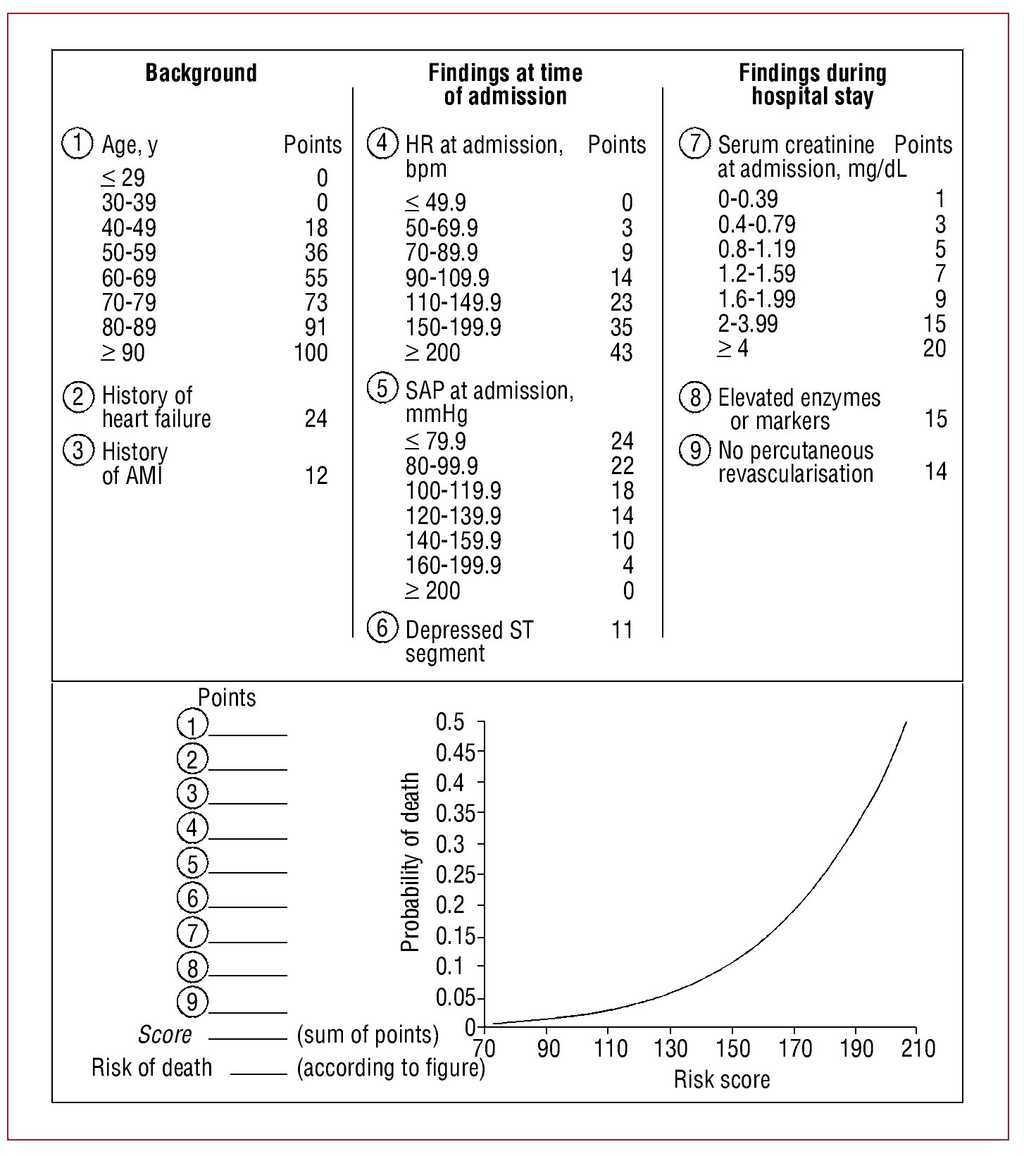
Validation Of The Grace Risk Score For Predicting Death Within 6 Months Of Follow Up In A Contemporary Cohort Of Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition
Non St Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes Unstable Angina And Non St Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Thoracic Key
Non Ste Acs Nstemi Ua Cardio Guide
Www Cardio Online Fr Content Download Version 1 File Heart Failure With Systolic Dysfunction Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction Pdf
Risk Stratification In Ua And Nstemi Why And How

Comparison Of The Grace Heart And Timi Score Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Receiver Operating Characteristic

High Risk Non St Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes Nsteacs For Paramedics Journal Of Paramedic Practice
Az Sponsors Heart Attack Risk App Pmlive
Www Escardio Org Static File Escardio Education Live Events Courses Education Resource 003 1300 Bassand Wbz Mon S01a Pdf
Www Acc Org Media Non Clinical Files Pdfs Excel Ms Word Etc Meetings 18 Course Pdfs Middle East Friday 1600 Acc10shaibi Pdf La En Hash 5fcf7e57babc2234facc4f8cbf232f122ab
Gale Onefile Health And Medicine Document Mortality Rate And Its Associated Factors In Patients With Non St Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome In Bali Results From A Single Center Registry

Acute Coronary Syndrome Current Treatment American Family Physician

Heart Rate N Variability Hrnv And Its Application To Risk Stratification Of Chest Pain Patients In The Emergency Department Biorxiv

Grace Risk Score And Outcomes Low Intermediate And High Categories Download Table

The Grace Score S Performance In Predicting In Hospital And 1 Year Outcome In The Era Of High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Assays And B Type Natriuretic Peptide Heart
Www Internationaljournalofcardiology Com Article S0167 5273 16 332 X Pdf
Grace Score Among Six Risk Scoring Systems Cadillac Pami Timi Dynamic Timi Zwolle Demonstrated The Best Predictive Value For Prediction Of Long Term Mortality In Patients With St Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Does Simplicity Compromise Accuracy In Acs Risk Prediction A Retrospective Analysis Of The Timi And Grace Risk Scores

Prediction Of Risk Of Death And Myocardial Infarction In The Six Months After Presentation With Acute Coronary Syndrome Prospective Multinational Observational Study Grace The Bmj

Risk Stratification For The Development Of Heart Failure After Acute Coronary Syndrome At The Time Of Hospital Discharge Predictive Ability Of Grace Risk Score Sciencedirect

Comparison Of The Grace Heart And Timi Score To Predict Major Adverse Cardiac Events In Chest Pain Patients At The Emergency Department J M Poldervaart Ppt Download

Pdf Comparing Heart Timi And Grace Scores For Prediction Of 30 Day Major Adverse Cardiac Events In High Acuity Chest Pain Patients In The Emergency Department
Www Heartfoundation Org Au Getmedia 8cbc027d B610 419a Be3b 717fadc061 Acs Guidelines Long Presentation 16 V2 1 Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcskjkg817zmnceno5yufrdxmvd5e756gibv 39kl4bgnmfk 67g Usqp Cau

Ukpds Risk Engine Overview

Traumagency The Heart Score

Timi Ua Nstemi Risk Score Download Table

Jpma Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association
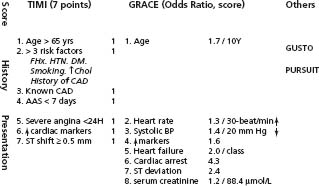
Timi Score And Grace Score Abbreviations Acs Acute Co Open I



